Information Storage and Retrieval System
Paper-M-108
7th May 2023
UNIT – I: Fundamental Concepts
- Concept, Characteristics, Objectives, Types, Operations and Design
- Compatibility of ISAR System
- Information Retrieval Process and Search Strategy
- Evaluation of ISAR System
- Vocabulary Control Tools: Classification Schedules, Subject Heading Lists and Thesaurus
- Need, Structure and Construction of Thesaurus
- Principles and Evolution of Bibliographic Description
Introduction to Information Retrieval
What Will You Learn - Part A?
- Basic concepts and history of Information Retrieval (IR)
- Familiarization with the essential functions of IR
- Familiarization with various applications of information retrieval system in various fields
Introduction
Data
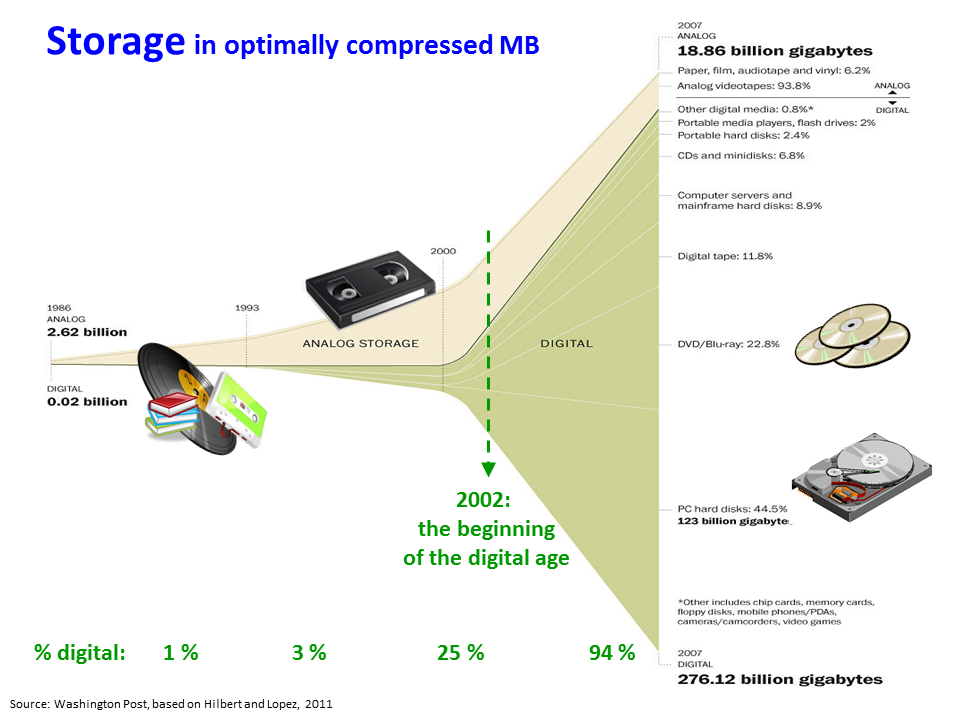
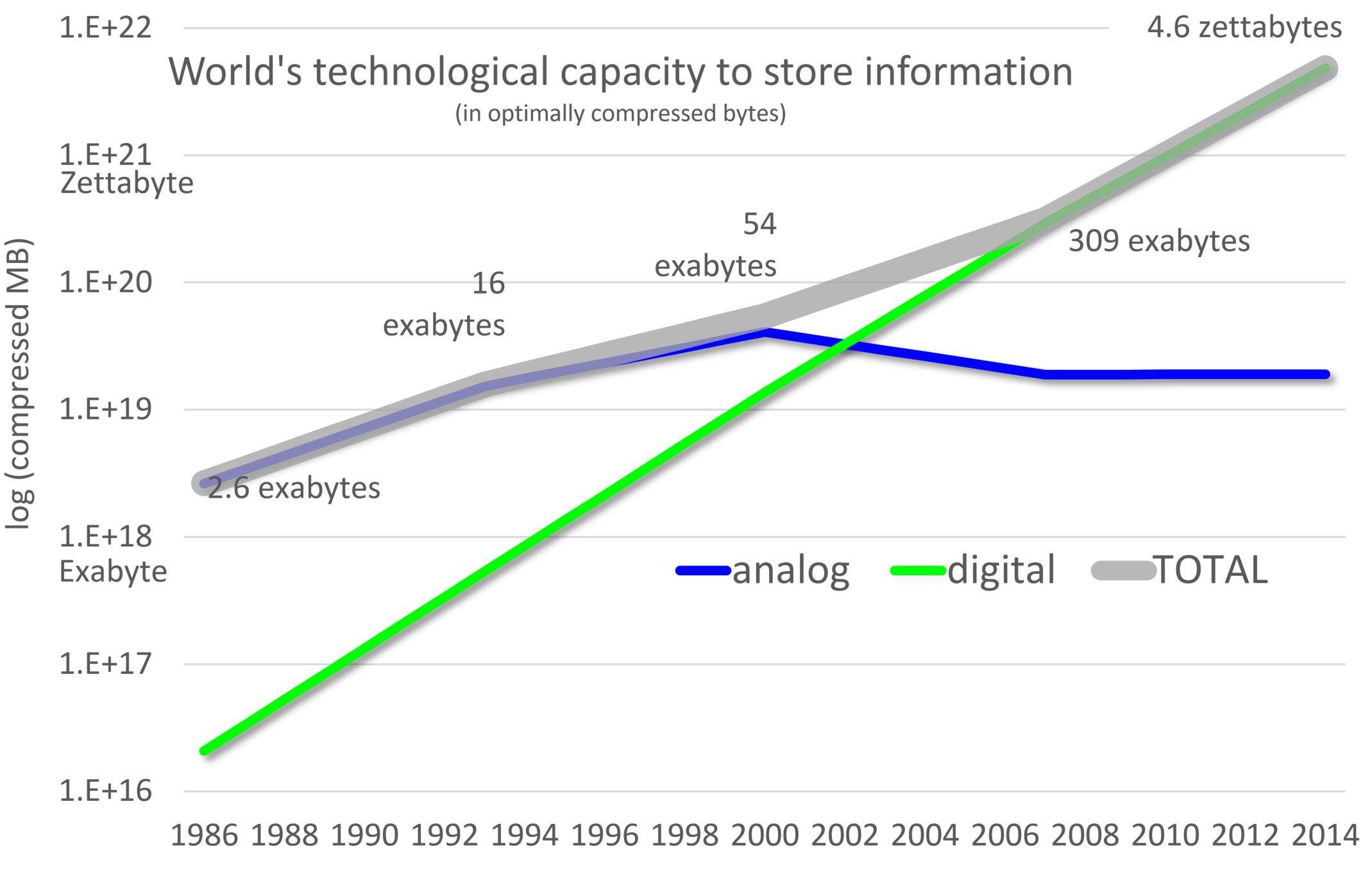
Data and information generation in every discipline in the universe of knowledge has seen staggering growth
Storing, managing, querying, & retrieval of huge amount of data & information needs sophisticated procedures & advanced technologies
Nowadays, information collection is web-based and online which is vast and growing at an exponential rate
Introduction (Cont.)
Challenges to IR
Information collection is very heterogeneous
Information need of a user is of complex nature
Many complex models have been developed to understand the information need of a human but it still remains a problem area that has many open questions that is unanswered (user behavior, query analysis):
How an end-user will seek information
How will they understand their information need
How they will go to a system & express their information need
Introduction (Cont.)
- How they attempt to retrieve something against that information need
User’s information need is continuously evolving according to the medium & collection itself
Users have very little time to retrieve complex material, formulate & refine their query
In such a situation, it becomes a huge IR challenge when we have a large evolving heterogeneous content on one hand and we have users with very complicated user query on other hand which has not given much time for retrieval. The challenges for IR are certainly are huge
Need of Information Retrieval
Size and number of documents increased where no traditional cataloging system can give technical support
Libraries had a little or limited scopes in terms documents processing, handling different e-resources or sharing heterogeneous data and information over the internet
Different disciplines (biotechnology, genetics, geoinformatics, etc.) started producing different types of data with computer support and in multiple number of file formats which need to be indexed, stored, organized, or retrieved. These data are mostly semi-structured (video, audio) or unstructured (webpages, e-resources)
Need of Information Retrieval (Cont.)
- On the web, different organization started publishing and sharing information which should be pre-processed, filtered and modeled to give a general structure in the web environment
But that is not happening. Different organizations just started publishing & populating documents as and when they can produce information
Wherein in a classic IR system, documents need to be indexed, scanned, coining certain information that goes to bibliographic elements (structured metadata)
Need of Information Retrieval (Cont.)
- But NO SUCH thing is available on the web, subsequently this big difference created a technical paradigm shift and necessitated to invent new theory and concepts to handle e-resources
- Librarian’s approach towards indexing is based on pre-coordination system and both success & efficiency of the indexing used to heavily depend on classification system
For example, based on colon classification, chain indexing system was developed by S.R. Ranganathan
Need of Information Retrieval (Cont.)
- But maintaining pre-coordinate indexing system costs an enormous human labour and also it lacks computation with mathematical or statistical approach. Unless the users know the proper index term needs to be given at search time, retrieval of relevant documents may be difficult
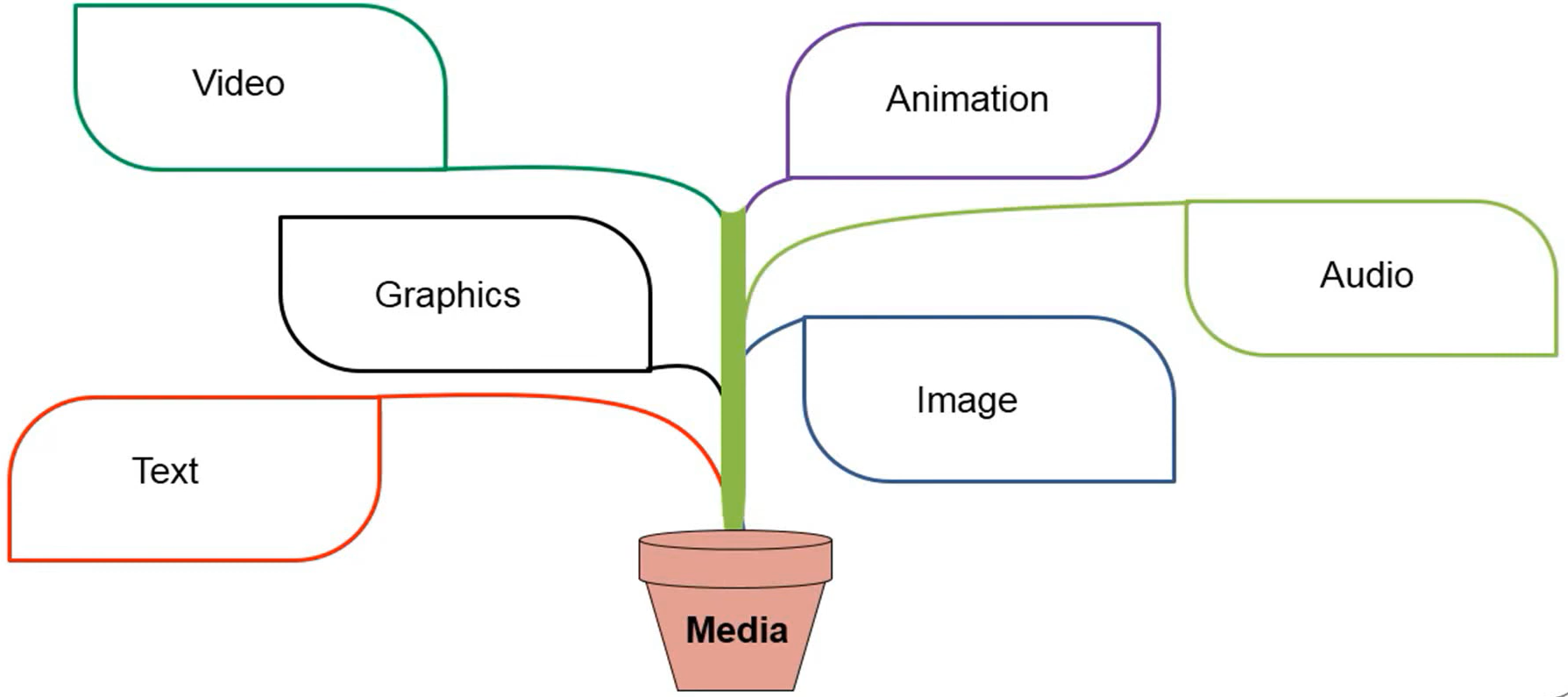
Different Forms of Media & Documents
- Media of Information
![]()
- Text
- Image
- Graphics
- Audio (Sound, Speech, Music)
- Video
- Animation
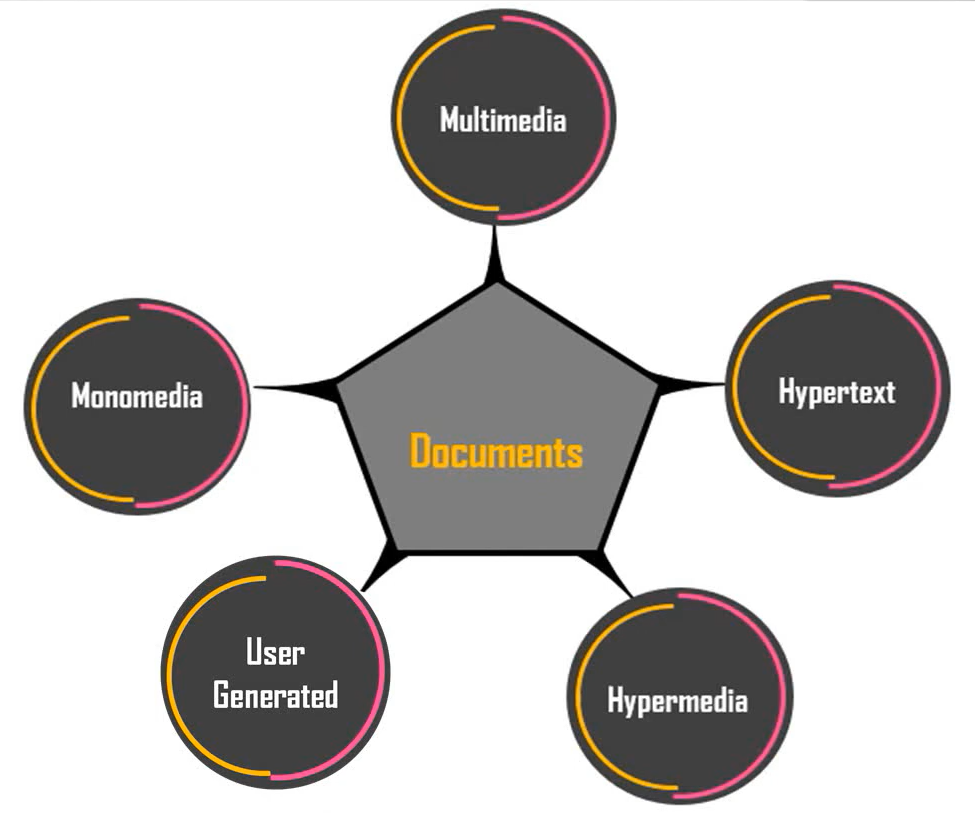
Different Forms of Media & Documents (Cont.)
- Document is a piece of written, printed or electronic matter the provides information or evidence or that serves as an official records
![]()
- Monomedia - Text, Documents, Official Records, etc.
- Multimedia - Documents with different media
- Hypertext - Documents with links
- Hypermedia - Multimedia + Hypertext
- User Generated - Blogs, Comments, Tweets
Quiz-1

What is Information Retrieval?
- Information Retrieval includes:
Representation
Storage
Organization
Document Clustering
Classification of Documents
System Architecture
Information & Data Visualization
Allied Services
Ranking of Documents
Semantic Linking
Filtering
Others
- Search engines have been developed based on the concepts, principles, and techniques developed by IR
What is Information Retrieval? (Cont.)
- Based on the different types of services of IR categorized as
Web Search
Personalized IR
Enterprise/Institutional IR
Domain-Specific IR
Web Based IR System
Digital Libraries
Multimedia IR System
Distributed IR System
Advantages of IR Systems
The importance of IR was felt when there was a necessity to locate or to get those shared information without restrictions
Advantages
It can accept queries in natural language and execute matching operation with its indexed term at back-end and locate the expected document from its term-document matrix.
After executing the queries, search engine represents the results with ranks as a specific ranking algorithm (e.g. Page Rank) runs on the fetched result. Preferably, the most relevant documents get top ranks than non-relevant ones.
Advantages of IR Systems (Cont.)
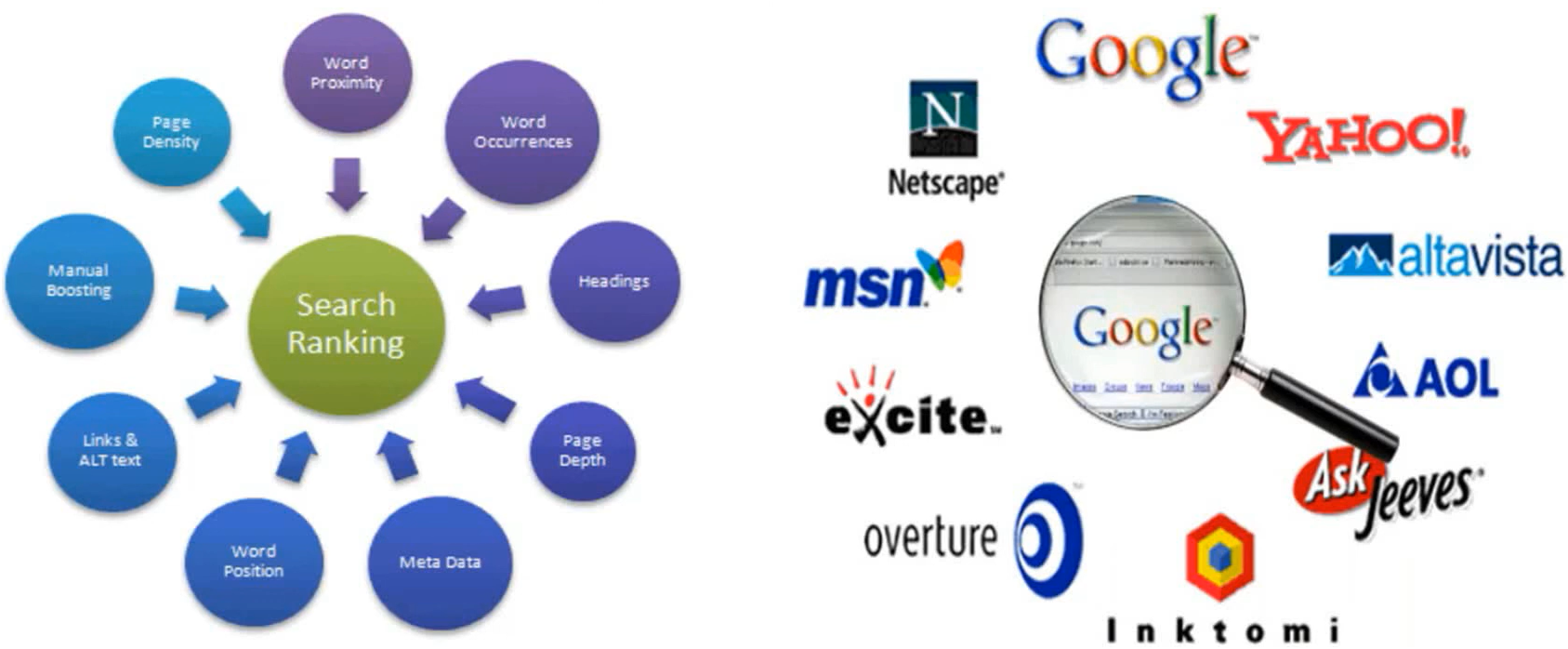
As most of the IR systems (Search Engines) index the documents on incremental basis, web-based crawlers crawl the web pages in the hyperspace within certain time interval and get the updated information and further index the crawled information. Thus, we get the latest information from the search spaces.
IR system has opened up huge business opportunities through web environment.
Brief History of Information Retrieval

Lamba, M., Madhusudhan, M. (2022). The Computational Library. In: Text Mining for Information Professionals. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85085-2_1
Brief History of Information Retrieval (Cont.)
System for the Mechanical Analysis and Retrieval of Text (SMART)
- SMART was developed by Gerard Salton in Cornell University in 1960s
- This system incorporated many important concepts like vector space model, relevance feedback, and Rocchio Classification
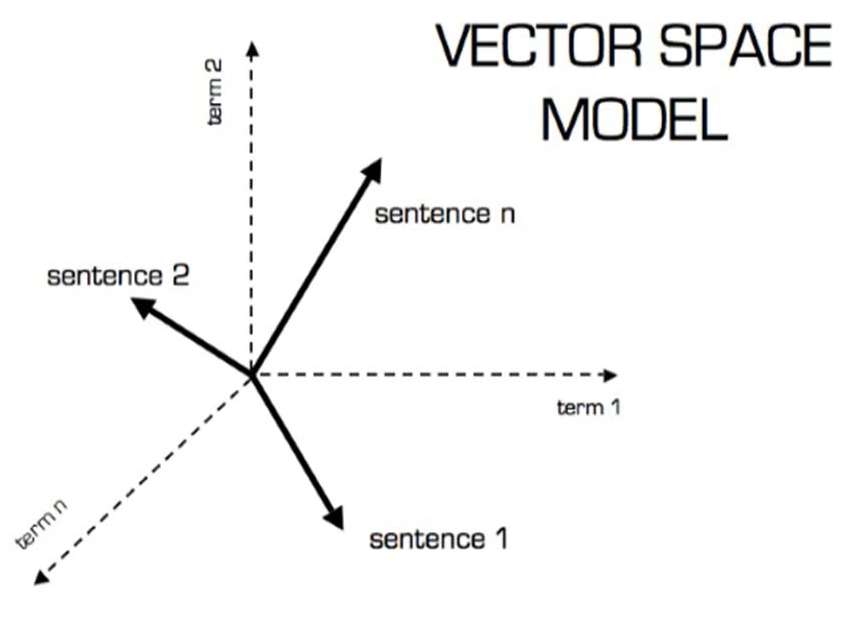
Brief History of Information Retrieval (Cont.)
J.W. Sammon (1969) gave the idea of visualization interface integrated to an IR system in his famous paper “A nonlinear mapping for data structure analysis”
First online systems–NLM’s AIM-TWX, MEDLINE; Lockheed’s Dialog; SDC’s ORBIT
 - During 1966-67, F.W. Lancaster evaluated the MEDLARS (Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System)
- During 1966-67, F.W. Lancaster evaluated the MEDLARS (Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System)
Brief History of Information Retrieval (Cont.)
AM SIGIR Conference started in 1978 which subsequently emerged as the apex conference in IR systems
Belkin, Oddy, and Brooks gave the concept of Anomalous State of Knowledge (ASK) for information retrieval in 1982
OKAPI model was formulated in 1982-88 which is a set-oriented ranked output design for probabilistic type retrieval of textual material using inverted index
Major breakthrough was in 1989 when Tim Berners-Lee proposed World Wide Web in CERN Laboratory
TREC conference started as part of TIPSTER text program in 1992 and it was sponsored by US Defense and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
Brief History of Information Retrieval (Cont.)
PageRank algorithm was developed at Stanford University by Larry Page and Sergey Brin in 1996
Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA), a generative/topic model in NLP was developed by David Blei, Andrew NG, and Michael Jordan in 2003
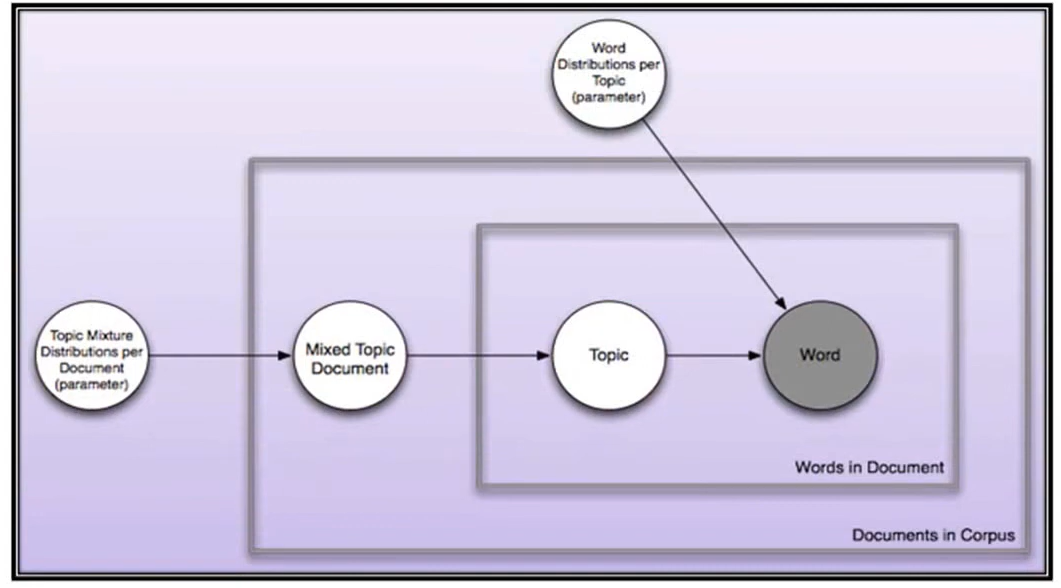
- LSI gained huge popularity in WWW and was hugely used in Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Brief History of Information Retrieval (Cont.)
In 1997, Google Inc. was born which has now ruling dominantly in searching engine domain
The present situation of web and the environment of search engine did not evolve within moments rather it’s the product of decades-long research
What Will You Learn - Part B?
- Introduction to the basic concepts of IR systems and their components
- Brief about methods that enable users to find out relevant information from an organized collections of resources
- Introduction to various features of IR systems that help in easy retrieval of documents from interdisciplinary field
- Introduction to different functions of IR system which deals with various format(i.e. text, audio, image, and video ) of information
Basic Concepts of IR systems
- Knowledge system into which an IR system is implanted to consist of three of component parts:
people in their role as information-processors
documents in their role as carriers of information
topics as representations
IRS does not inform the user on the subject of their inquiry, it merely informs them of the existence (or non-existence) and whereabouts of documents relating to their request (Lancaster)
This notion changed of IR changed since the availability of full-text documents in bibliographic databases
Basic Concepts of IR systems (Cont.)
IRS originally meant text retrieval systems, since they were dealing with textual documents
Many modern information retrieval systems deal with multimedia information comprising text, audio, images and video
Specific nature of audio, image and video information has called for the development of many new tools and techniques for information retrieval
Modern information retrieval deals with storage, organization and access to text, as well as multimedia information resources
Features of IR Systems
An IRS is developed to help users to discovery relevant information from a storehouse containing collection of documents
The idea of information retrieval assumes that there exist several documents or records comprising data that have been arranged in a suitable order for easy retrieval
The storehouse contains many bibliographic information, which is quite different from other kinds of information or data
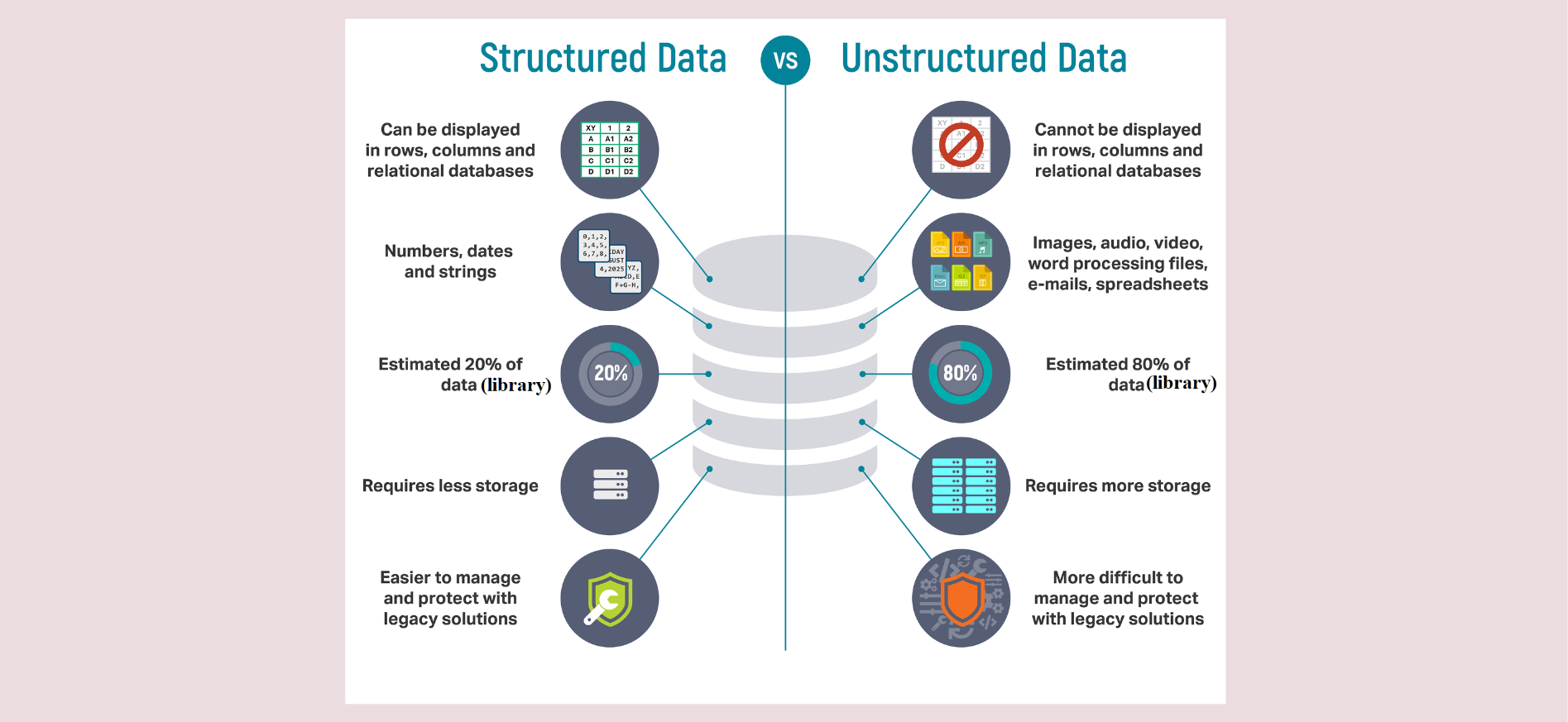
Conventional database management systems, such as Access, Oracle, MySQL, etc, deal with structured data, where the arrangement/structuring of data is based on the specific attributes of data elements
Features of IR Systems (Cont.)
The main objective of these databases is to enable the user to search for specific records that be matched with one or more specific conditions or search criteria usually laid by users in an online environment
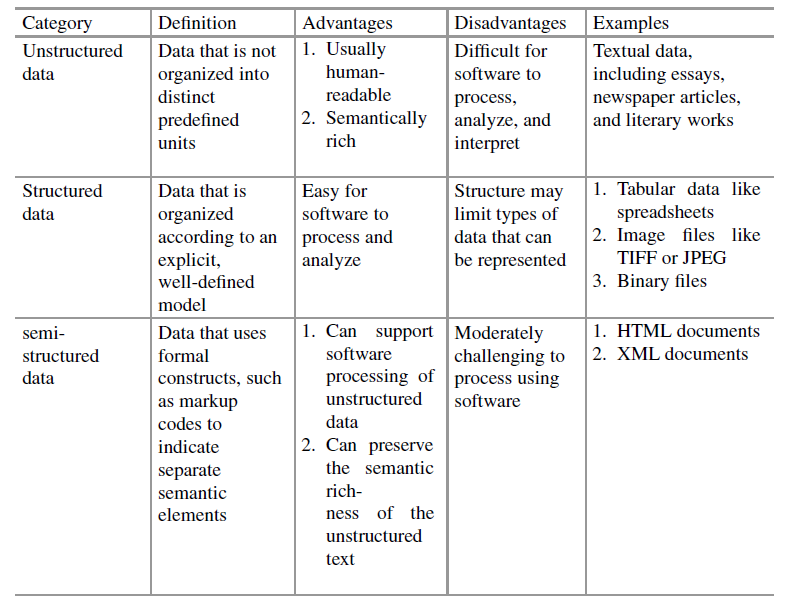
Unlike a conventional database management system (DBS), an IRS deals with unstructured data
Main purpose of designing an IRS is to answer to the users’ queries
Retrieved information can be in represented in different forms: text along with video, audio, images, graphics, animations
Scope of IR System
- IRS and database systems merely find what already is there. It does not invent anything new by itself
- Whatever is there and whatever is already represented in a form, IR system can retrieve it
Types of IR System
Most IR research focuses more specifically on text retrieval – the computerized retrieval of machine-readable text without human indexing
But it has spread across other interesting areas such as
- Speech Retrieval - It includes several well-established speech signal analysis research fields such as speech recognition, speaker identification, voice detection, sentiment analysis and fingerpring
Types of IR System (Cont.)
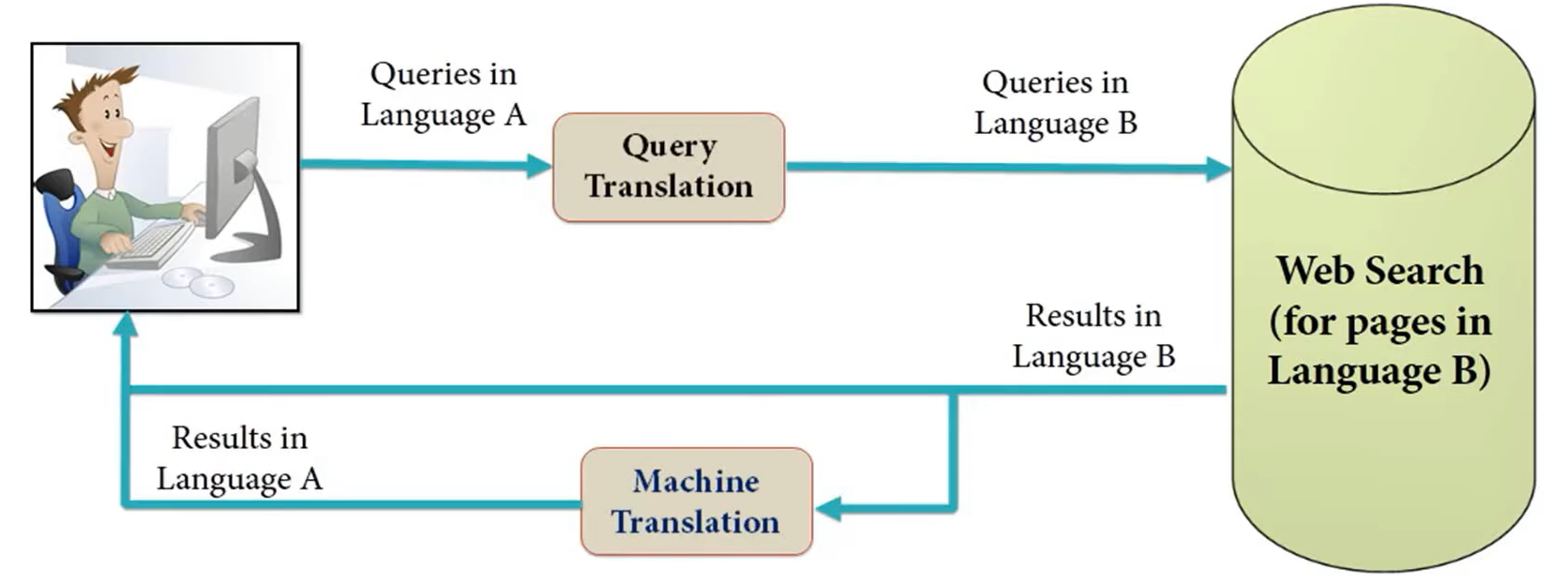
- Cross language information retrieval - It deals with fetching information written in a particular language different from the language of the user’s query
Types of IR System (Cont.)
- Question-answering IRS - It is a computer science discipline within the domains of information retrieval and natural language processing (NLP), which is involved with building systems that automatically answer questions posed by humans in a natural language.
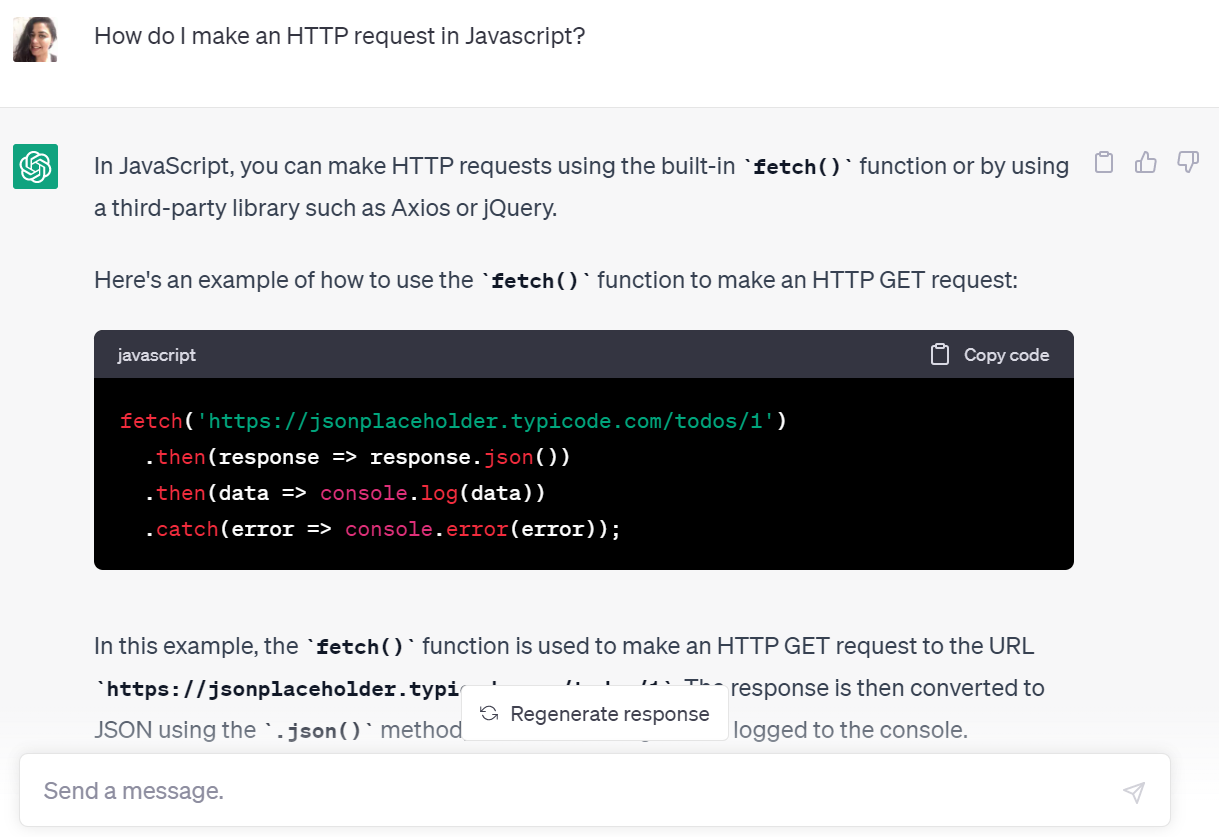 - QA systems can pull answers from an unstructured collection of natural language documents. Eg. ChatGPT, Chatbots
- QA systems can pull answers from an unstructured collection of natural language documents. Eg. ChatGPT, Chatbots
Types of IR System (Cont.)
Image Retrieval - It helps the retrieval system for browsing, searching and retrieving images from a large database. The database may contain only digital images, images along with text
Music Retrieval - It is a small yet it is a growing field of research with many real-world applications
Functions of IR System
An information system essentially makes ensure that users should be satisfied with the service.
The system will be able to accomplish tasks, solve problems, and make decisions, based on the user needs. In short, an IRS should:

Functions of IR System (Cont.)
All operations pertaining to information retrieval surround around usefulness and relevance of documents.
The use of a document is dependent upon on three major things, topical connectedness, applicability, and originality.
A resource is considered to be topically significant for a particular context, question, or task if it consists of information that either instantly provides answer to the query or can be used, in combination with other information, to infer an answer or perform the task.
Functions of IR System (Cont.)
The appropriateness of the answer completely depends upon the user for a given context.
It is original if it provides an input to the user’s knowledge.
Evaluation/Utility of IR System
Utility can be measured in monetary terms: “To what extent the document is useful for the user?”, “What is the recall and precision of the search engine”?
The term “relevance” can indicate utility or topical relevance or pertinence. Many IR systems focus on finding topically relevant documents, leaving further selection to the user.
Relevance is a matter of degree. Some documents are highly relevant and indispensable for the user as it serves the purpose of the users’ need; others may not contribute much to the users’ requirements.
Evaluation/Utility of IR System (Cont.)
- From relevance assessments, measures of retrieval performance can be computed such as,

Evaluation/Utility of IR System (Cont.)
- Evaluation studies normally use recall and precision or a combination of both; but there exists a lot of argument whether these can be considered as the best measures for information retrieval systems
Basic Steps of IR
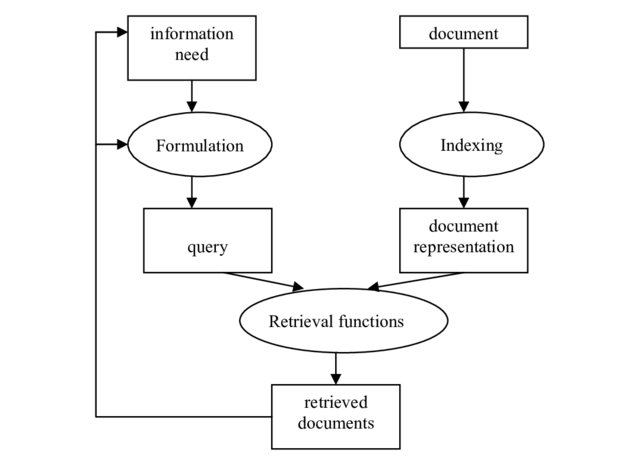
Basic Steps of IR (Cont.)
Analysis - Analyzing the available content in the information sources as well as the queries
Matching - Matching the user’s query with the available document in order to retrieve relevant resources
Functions of IR
To identify the information sources relevant to the areas of interest of the target user’s community
To analyze the contents of the sources (documents)
To represent the contents of analyzed sources in a way that matches users’ queries
To analyze users’ queries and represent them in a form that will be suitable for matching the database
To match the search statement with the stored database
To retrieve relevant information
To make continuous changes in all aspects of the system
Questions
Q1. What do you understand by ‘Information Retrieval’? Discuss the various components and types of Information Retrieval System. (12.5 Marks)
Q2. ‘Evaluation is the best process to ascertain the merits and demerits of Information Storage and Retrieval System’. In light of the statement, discuss the criteria used for evaluation of an Information Retrieval System. (12.5 Marks)